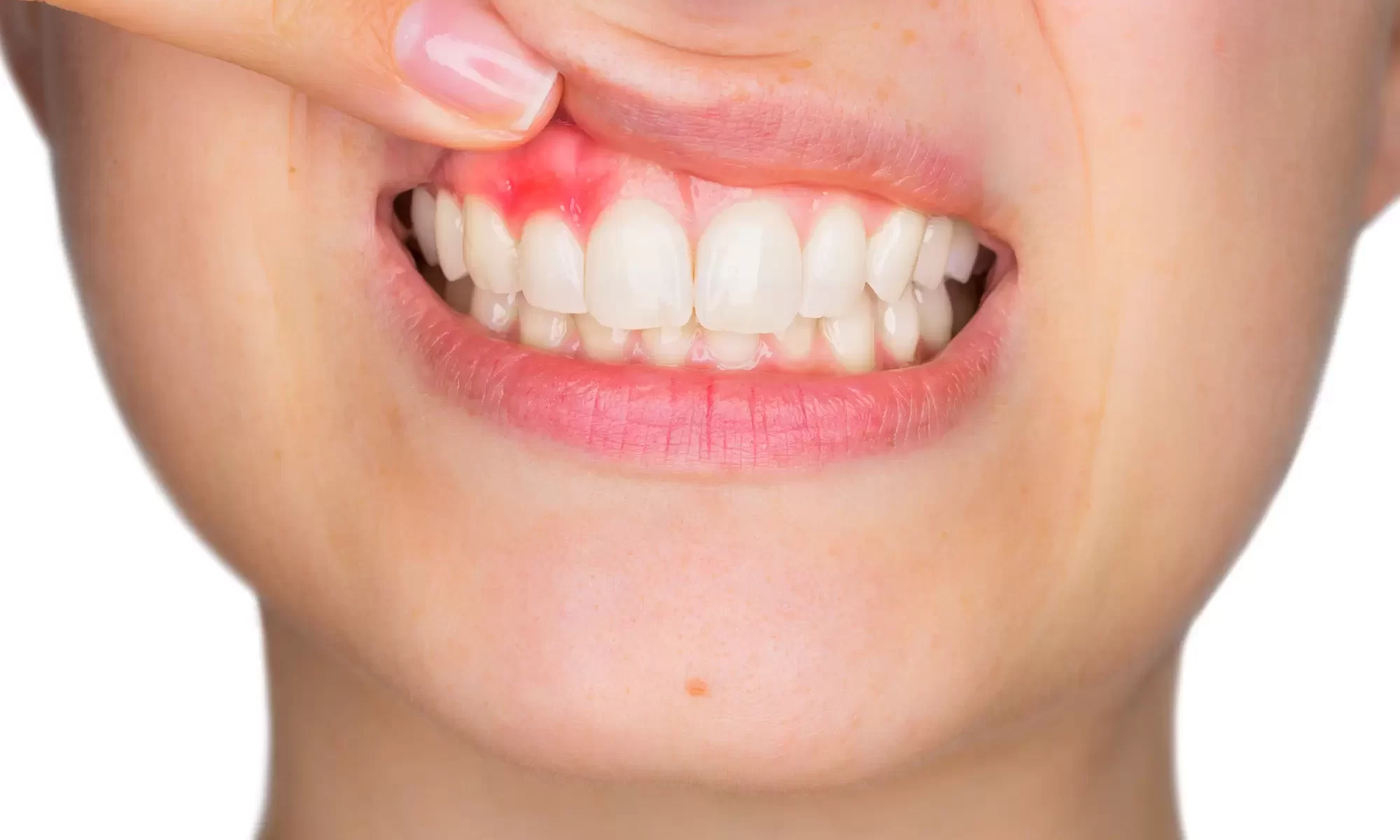
Gingivitis or bleeding gums is a common dental condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It refers to inflammation of the gums, primarily caused by poor oral hygiene. While gingivitis may seem like a minor issue, if left untreated, it can progress into a more serious condition known as periodontitis, which can result in tooth loss and other complications. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gingivitis, shedding light on how to prevent and manage this oral health concern.
Causes of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque on the teeth and gumline. Plaque is a sticky film composed of bacteria, food particles, and saliva. When plaque is not adequately removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar (calculus), which harbors more bacteria and irritates the gums. Additionally, certain factors increase the risk of developing gingivitis, including:
Poor oral hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up, leading to gingivitis.
Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can make gums more susceptible to inflammation.
Medications: Some medications can reduce saliva flow, leading to dry mouth, which increases the risk of gingivitis.
Smoking: Tobacco use weakens the immune system and hampers gum tissue’s ability to heal, making smokers more prone to gingivitis.
Genetics: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to gum disease, including gingivitis.
Vitamin C deficiency: Vitamin C is an essential nutrient that supports the production of collagen, a protein that helps in the formation and maintenance of healthy gum tissue. When the body lacks vitamin C, the gum tissues become weaker and more susceptible to infection and inflammation. This weakened gum tissue allows bacteria to penetrate more easily, leading to the onset of gingivitis.
Symptoms of Gingivitis

Recognizing the symptoms of gingivitis is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment. Common signs and symptoms include:
Red and swollen gums: Gingivitis causes the gums to appear inflamed and puffy, instead of their healthy pink color.
Bleeding gums: Gums that bleed easily, especially during brushing or flossing, are an indication of gingivitis.
Bad breath: The accumulation of bacteria in the mouth due to gingivitis can cause persistent bad breath (halitosis).
Receding gums: As gingivitis progresses, the gums may begin to recede, making the teeth appear longer.
Tender gums: Gingivitis can cause discomfort or tenderness in the gums, particularly when pressure is applied.
Treatment and Prevention

Fortunately, gingivitis is reversible with proper treatment and preventive measures. Here are some strategies to manage and prevent gingivitis:
Good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Don’t forget to floss daily to remove plaque and debris from between the teeth.
Regular dental check-ups: Visit your dentist for regular cleanings and check-ups to monitor your oral health and address any early signs of gum disease.
Professional cleaning: In cases of gingivitis, your dentist or dental hygienist may perform a professional cleaning, known as scaling and root planing, to remove plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline.
Antimicrobial mouthwash: Rinsing with an antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria in the mouth and control gum inflammation.
Quit smoking: If you smoke, quitting can significantly improve your gum health and reduce the risk of gingivitis.
Healthy lifestyle choices: A balanced diet, rich in fruits and vegetables, can boost your immune system and promote oral health.
Get Your Vitamin C: To prevent gingivitis and maintain healthy gums, it is essential to consume an adequate amount of vitamin C through a balanced diet. Excellent sources of vitamin C include citrus fruits (such as oranges and grapefruits), strawberries, kiwi, bell peppers, broccoli, and leafy greens. In some cases, when dietary intake is insufficient, a healthcare professional may recommend vitamin C supplements.
However, it is important to note that vitamin C alone cannot prevent or cure gingivitis. Good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, are equally crucial. Combining these practices with a balanced diet rich in vitamin C can significantly reduce the risk of gingivitis and support overall oral health.
Natural remedies for Gingivitis
While it’s important to consult a dental professional for proper diagnosis and treatment of gingivitis, there are some natural remedies that can complement conventional therapies and promote gum health. Here are five natural remedies that may help in managing gingivitis:
Saltwater Rinse
A saltwater rinse can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria in the mouth. Dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in warm water and swish the solution around your mouth for about 30 seconds. Spit it out and repeat a few times a day to soothe irritated gums.
Oil Pulling
Oil pulling involves swishing oil in your mouth to remove bacteria and promote oral health. Coconut oil is commonly used for this purpose. Take a tablespoon of coconut oil and swish it around in your mouth for 15-20 minutes before spitting it out. Rinse your mouth with water and brush your teeth as usual. Oil pulling can be done once a day.
Aloe Vera
Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, which can help reduce gum inflammation and fight off bacteria. Apply a small amount of aloe vera gel directly to your gums and gently massage it in. Alternatively, rinse your mouth with aloe vera juice. Repeat a few times a day.
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil has natural antiseptic properties that can help combat bacteria associated with gingivitis. Dilute a drop or two of tea tree oil in a tablespoon of water and use it as a mouthwash. Swish the mixture in your mouth for about 30 seconds and spit it out. It’s important not to swallow tea tree oil as it can be toxic. Use this mouthwash once daily.
Turmeric Paste
Turmeric possesses anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties that may aid in reducing gum inflammation. Make a paste by mixing turmeric powder with water or coconut oil. Apply the paste directly to your gums and let it sit for a few minutes before rinsing your mouth thoroughly. Use this remedy a few times a week.
Conclusion
Gingivitis is a common and preventable dental condition that can lead to more severe complications if left untreated. By practicing good oral hygiene, visiting your dentist regularly, and making healthy lifestyle choices, you can effectively manage and prevent gingivitis. Remember, early detection and prompt treatment are key to preserving your gum health and maintaining a beautiful smile. Take charge of your oral hygiene today and enjoy a lifetime of healthy gums and teeth. If you suspect you have gingivitis or are concerned about your gum health, it is recommended to consult with a dental professional who can provide a proper diagnosis and develop a personalized treatment plan.